UA to GA4: what's changed for marketing teams?
It’s happening. Starting from 1 July 2023, Google Analytics will be changing from Universal Analytics (UA) to GA4, a new version of Google’s analytics platform. This change is mandatory for all GA users, and with it comes new features and functionalities to help you better understand your website’s performance. Google has a lot of documentation on making the switch, but I decided to create a quick summary of it to get your team started.
The main benefits of transitioning to GA4
- It’s recommended to switch to GA4 from Universal Analytics as soon as possible for better data comparison and tracking optimization. Migrating sooner to Google Analytics 4 will also give you access to more historical data and insights. Google will still support UA historical data until January 1st 2024 and afterward delete all UA data. Early migration will ensure a smoother transition and familiarize your team with GA4’s workings.
- Machine learning algorithms: GA4 uses machine learning to provide insights and predict the future behavior of your users. This is great for optimizing your growth strategy towards certain user trends on your app/website. It helps you forecast purchase probability, in-app purchase probability, and churn probability. By leveraging these metrics, you can also create predictive audiences, which is a new way to target prospects with paid ads.
- Cross-platform tracking: GA4 supports cross-platform tracking capabilities, allowing for the collection and analysis of data from various devices and platforms, such as websites, mobile apps, and smart speakers. This provides a more comprehensive understanding of customer journeys and behavior across multiple touchpoints.
- User-centric approach and segmentation: GA4 has a user-centric approach, allowing for more complex buyer journeys to be analyzed and understood. This includes the ability to segment users based on their behavior and characteristics, providing a more in-depth understanding of your target audience.
- Advanced analysis reports: GA4 provides advanced analysis reports, including real-time reports, conversion reports, and event reports, that offer a more in-depth and sophisticated understanding of your data. These reports allow for a deeper understanding of customer behavior, conversion funnels, and the impact of marketing efforts.
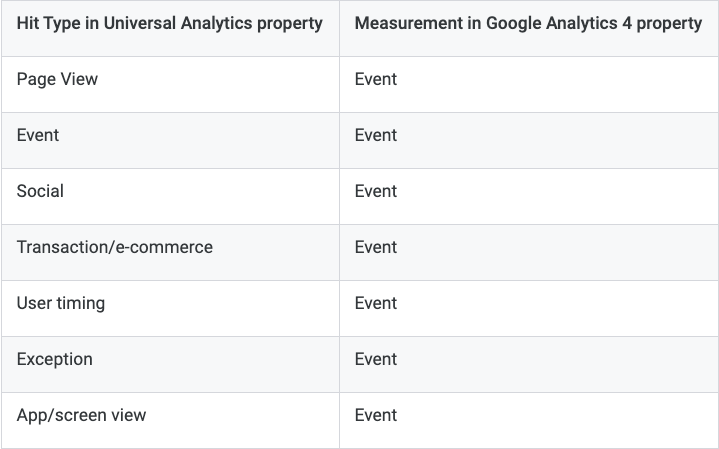
- Events-based goals: In GA4, there is no distinction between goals and e-commerce. You measure all conversions via GA4 events. GA4 events are triggered as users interact with your site or app. Using the user interface, you flag any events that contribute to the success of your business as conversions. Whenever any of these flagged events is triggered, a conversion is registered in your GA4 property.


Overcoming the current GA4 hurdles
- Reporting delay: GA4 introduces a delay in reporting of up to 24h-48h, meaning that data may not be available for analysis immediately, which can impact real-time decision-making.
- Check your 3rd party integrations: GA4 may have compatibility issues with third-party tools and integrations, requiring manual updates and configurations to ensure proper data tracking and reporting.
- Limited importing of paid ads costs: GA4 currently has limitations in importing cost data for paid advertising campaigns, requiring manual data entry or the use of a third-party tool for accurate cost analysis.
- E-commerce data collection set up: GA4 lacks an in-built e-commerce tracking feature, requiring the manual setup of e-commerce events and funnels or the use of a third-party extension for your e-commerce platform. You’ll need to create key e-commerce events manually in Google Tag Manager as custom events to allow for analysis of user shopping behavior in GA4 reports.
- Experiment with reporting options: GA4 offers a range of reporting options, including real-time reports, conversion reports, and event reports, that provide different perspectives and insights into your data.
- A difference in attribution model: GA4 uses a different attribution model compared to Universal Analytics, which may impact the way that conversions and revenue are attributed to different touchpoints in the customer journey.
- Default data retention: GA4 has a default data retention period of 14 months, meaning that data older than 14 months will be automatically deleted. It is important to consider this in your data management and reporting process and to configure the retention period as needed.
Nevertheless the challenges, GA4 is given and it’s recommended to use the UA & GA4 tandem as soon as possible. Are you ready to level up your analytics with GA4? Let’s get started.
The next generation of Google Analytics, implementing Google Analytics 4 for marketing teams
GA4 migration guide: How to make the transition from UA to GA4
STEP 1: Create your migration plan
It’s recommended to document all goals, events and settings that you have in Universal Analytics and Google Tag Manager, as well as other connected tools. This way, you get a full scope of what needs to be checked after making the migration to GA4.
- For new users: set up Analytics data collection for the first time.
- For UA users: Add Google Analytics 4 to a site with Universal Analytics. This way you collect data in both Analytics tools and can make the migration.
- For CMS users: Add Google Analytics 4 to a website builder platform or CMS. This sometimes requires a bit of a different implementation as a CMS usually supports analytics implementation as a feature or via plugins.
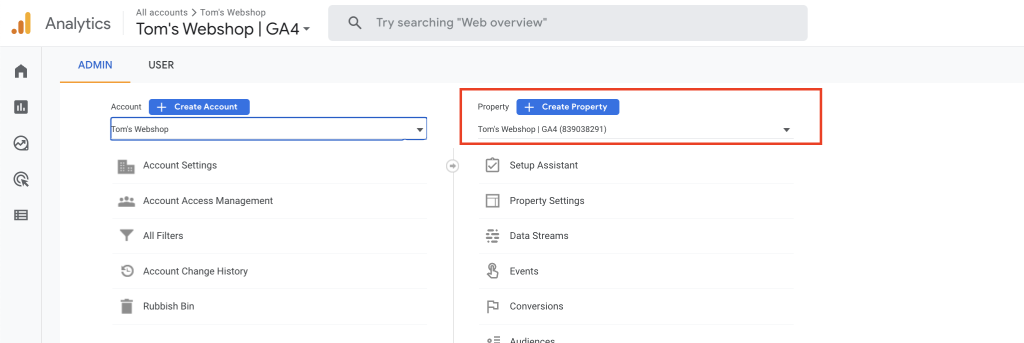


STEP 3: Set up the necessary data streams and start tracking.
For every environment you need to track, you’ll need to create a new data stream. In Admin, make sure you have your desired property selected and create a new data stream by following the steps.
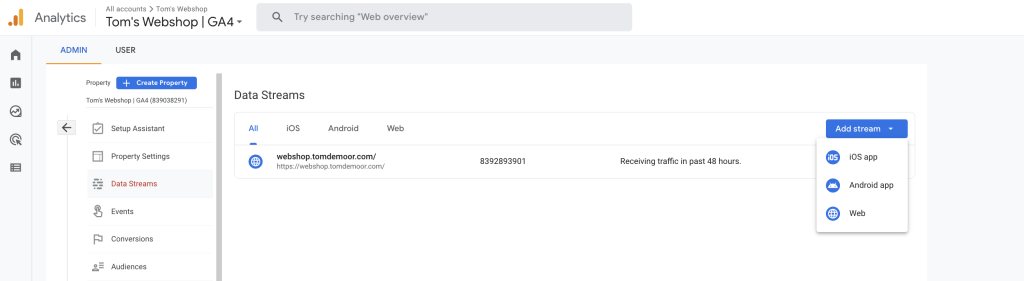


To set-up GA4 tracking for marketing teams, I recommend working with Google Tag Manager. Now that you have your GA4 property and data streams, it is ready to be implemented on your website. Here is the official video from Google Analytics on how to create a data stream and add GA4 to your website. If you are used to working with Google Analytics and GTM, this will be very easy.
Followed these steps? Great! You are now running basic user tracking. Data collection may take up to 30 minutes before starting. You can then use the Realtime report to confirm receipt of data.
STEP 4: Importing historical data from the UA property
Historical data from Universal Analytics can be migrated to Google Analytics 4 (GA4) with the help of Google Analytics 360, Google Tag Manager, and Google BigQuery, or third-party tools like Segment. The process involves exporting data from UA, transforming it to match GA4’s data schema, and loading it into BigQuery.
Although the process can be complex, it ensures all data attributes are preserved. If it’s not worth it for your team to invest in migration, it’s recommended to start dual tagging and collect data in both UA and GA4 as soon as possible.
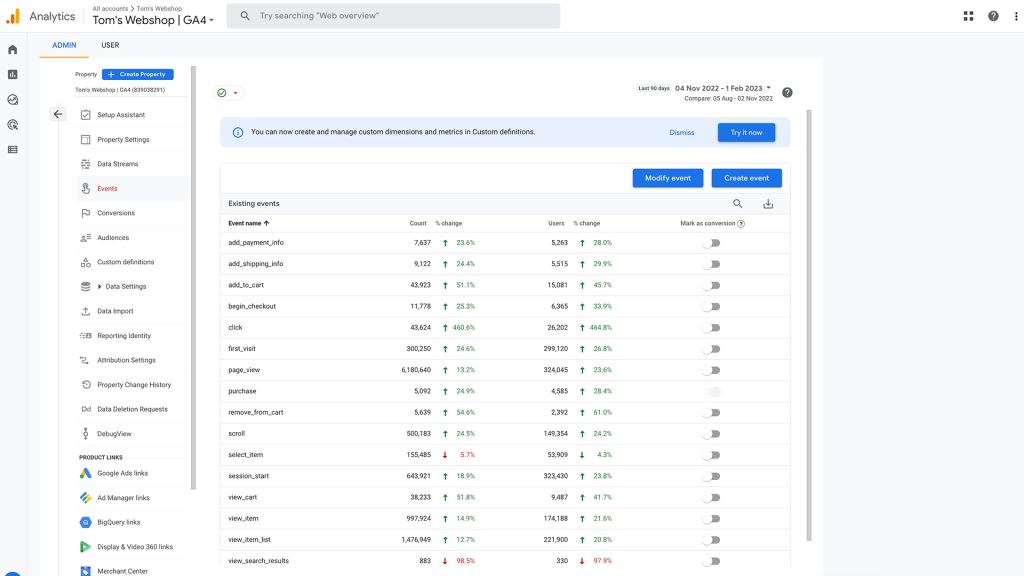
Though importing historical data to GA4 is challenging, there is good news! It’s easier to convert your goals.
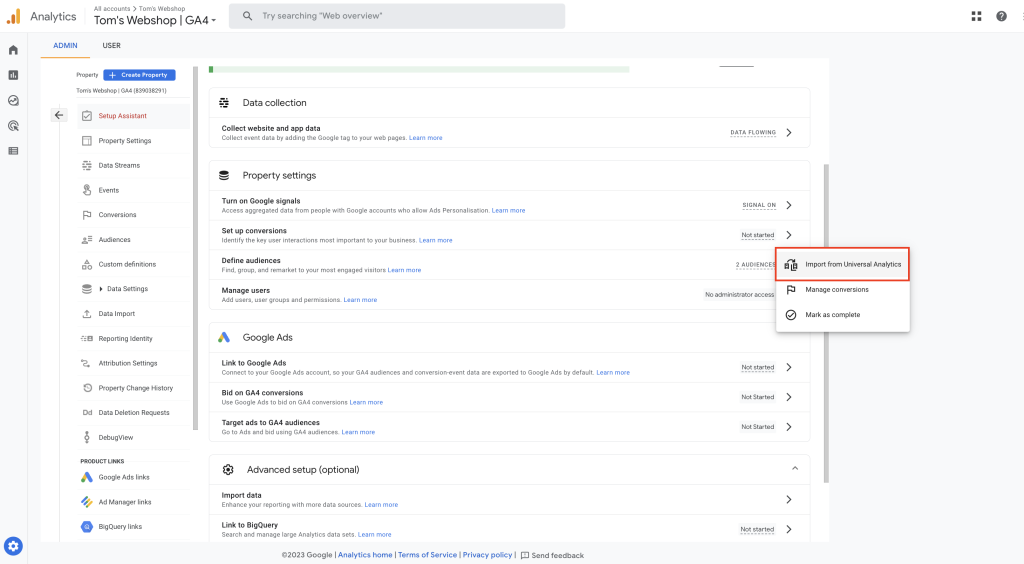


Under the events section, events can be marked as conversions. These will be the most important goals for your website. Here’s an example with dummy data.


STEP 6: Compare the UA and GA4 data
After migrating from UA to GA4, compare data in both platforms to ensure successful migration and correct data attributes. Review reports and data sets, identify differences, and address discrepancies. Regular monitoring and comparison can also ensure data quality.
STEP 7: GA4 reports
After migrating from Universal Analytics (UA) to Google Analytics 4 (GA4), it is important to start using the GA4 reports to gain insights into your data and make informed decisions.
GA4 offers a range of new and improved reports and features, including real-time event reporting, enhanced cross-device and cross-platform measurement, and automated insights. By using the GA4 reports, you can gain deeper insights into your data, understand user behavior, and optimize your website or app to drive better business outcomes.
It is recommended to familiarize yourself with the GA4 reports and features, and to use them regularly to make data-driven decisions and optimize your digital properties. I loaded in some dummy data below as a report example.
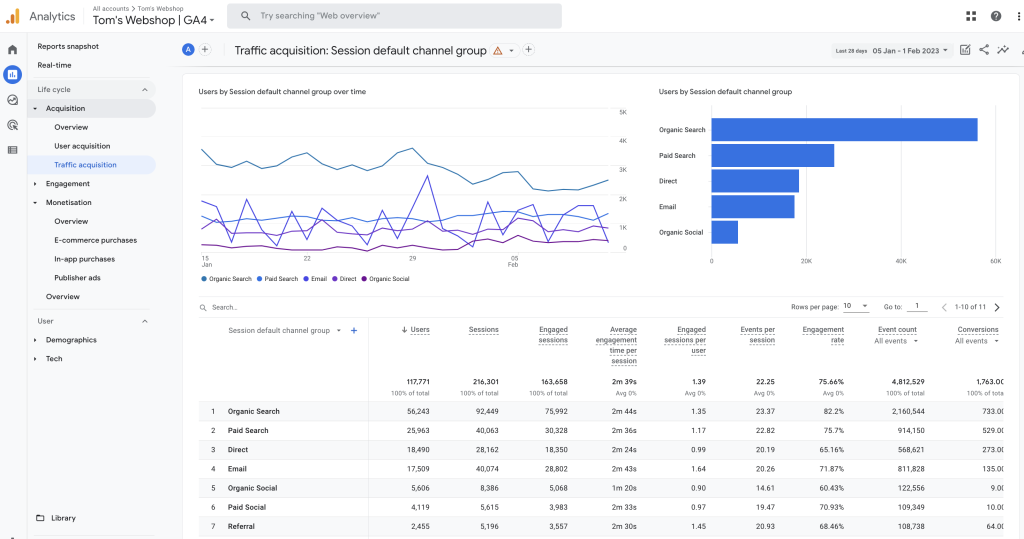


STEP 8: (dis)continuation of UA
In the end, when GA4 is running correctly, it is up to you when your team wants to stop collecting data with UA. As Thanos would say in The Avengers… It’s inevitable. I’d recommend keeping it up as long as possible, dual tagging and benefiting both systems to make sure to be prepared for any steps Google might take in the future.
- Keep improving tracking and goal setting to get the most correct data. Optimizing your data streams, creating views, etc. is a big part of this.
- Creating a dashboard, for example with Databox, that integrates data with your paid channels, or other channels to get a clear overview of the full customer journey.
- Create custom reports that are tailored to your specific needs and requirements, and use them to gain deeper insights into your data.
- Using this data to make informed decisions about KPIs and improve your growth marketing strategy.
Support
If you liked the article sharing it on LinkedIn is really appreciated. Thank You!